
How to Avoid Run-On Sentences and Fragments
The Role of Adverbs in Clear Communication
The Role of Adverbs in Clear Communication – When it comes to writing or speaking, the choice of words can make a huge difference. While nouns and verbs often grab the spotlight, adverbs play an equally important role. These small words may seem minor, but they can dramatically shape how your message is perceived. Understanding the role of adverbs can improve clarity, make your sentences more engaging, and help you communicate effectively in both personal and professional contexts.
What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They often provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. Common examples include words like quickly, slowly, very, always, and sometimes.
Unlike adjectives, which describe nouns, adverbs add context to actions and qualities. For instance, consider the difference between “She sings” and “She sings beautifully.” The adverb beautifully tells us more about how she sings, giving the listener or reader a clearer picture. Without adverbs, communication can feel flat or incomplete.
Why Adverbs Matter for Clear Communication
Clarity is key when conveying any message. Adverbs help achieve that by refining meaning and reducing ambiguity. For example, the sentence “He runs” is accurate but vague. If you say, “He runs quickly,” you immediately give the audience a better understanding of the action.
Adverbs also contribute to tone and emotion. Saying “I am extremely excited” conveys a stronger emotion than simply “I am excited.” This subtle shift makes your writing or speech more relatable and engaging.
Using Adverbs to Enhance Writing
Adverbs are not just about adding information; they can also improve the rhythm and flow of sentences. In storytelling or content writing, adverbs help create vivid imagery. Consider: “The cat silently crept across the room.” The adverb silently sets a mood and paints a clearer picture in the reader’s mind.
However, using too many adverbs or relying on them as a crutch can weaken your writing. Phrases like “very good” or “really bad” are less effective than more precise word choices. For instance, instead of “very happy,” using ecstatic conveys the emotion more strongly without extra words. The key is balance: use adverbs when they add clarity or emotion, but avoid overloading sentences with them.
Adverbs and SEO Writing for PBNs
In the world of content marketing, especially for private blog networks (PBNs), adverbs can subtly influence how readers engage with your content. High-quality, readable content ranks better on search engines, and adverbs help make sentences smoother and more natural.
Search engines favor content that flows naturally and keeps readers engaged. Consider the difference between “Our product works fast” and “Our product works incredibly fast.” The latter is more engaging, likely keeping the reader on the page longer, which is a positive signal for SEO. Using adverbs thoughtfully can enhance readability and improve user experience on your PBN sites.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even though adverbs are useful, there are common mistakes writers make. Overusing adverbs, especially in SEO content, can make your writing feel repetitive or artificial. Phrases like “very interesting” or “really amazing” may not add much value and can make the text less professional.
Another mistake is placing adverbs in awkward positions. For example, “She quickly ran to the store” works well, but “She ran to the store quickly” can sometimes disrupt sentence flow depending on context. Paying attention to placement ensures that adverbs enhance rather than hinder clarity.
Tips for Using Adverbs Effectively
To make the most of adverbs, start by identifying the purpose of each sentence. Ask yourself: does the adverb clarify meaning, set a tone, or emphasize a point? If the answer is yes, keep it. If not, consider removing or replacing it with a stronger verb or adjective.
Mixing adverbs with strong verbs often reduces the need for excessive description. For example, instead of saying “He ran very fast,” you could say “He sprinted.” This not only makes your writing more concise but also more impactful.
Adverbs in Professional Communication
Adverbs are not just for creative writing—they play a vital role in professional communication. Whether crafting emails, reports, or presentations, the right adverb can make your message more precise. Saying “We need to address this issue immediately” is more urgent than “We need to address this issue.”
Using adverbs in moderation ensures that your communication remains clear and persuasive without sounding exaggerated. Professionals who master this balance often find that their instructions and ideas are easier to follow and act upon.
The Subtle Power of Adverbs
Although small, adverbs wield significant power in communication. They can transform vague statements into precise descriptions, create tone and emotion, and improve engagement with your audience. For PBN content creators, understanding how to use adverbs effectively can enhance readability, boost SEO performance, and make content feel more authentic.
Learning to use adverbs skillfully is about practice and awareness. Read your sentences aloud and listen for clarity and flow. Replace weak adverbs with stronger verbs when possible, and always prioritize natural, reader-friendly writing. Over time, the right adverbs will become a subtle but essential part of your writing toolkit.
Conclusion
Adverbs may seem small, but their impact is anything but. From improving clarity and setting tone to enhancing SEO-friendly content for PBNs, they play a crucial role in effective communication. By understanding their function and using them thoughtfully, you can make your writing more precise, engaging, and enjoyable to read.
Clear communication doesn’t happen by accident—it’s built word by word. With a mindful approach to adverbs, your content can connect more deeply with readers while keeping your PBN sites optimized for search engines. The next time you write, pay attention to those small words—they might just make the biggest difference.

Understanding Parallel Structure in Sentences
Understanding Parallel Structure in Sentences – Writing that feels smooth and professional usually has one thing in common: balance. One of the most important techniques that creates this balance is parallel structure in sentences. If you’ve ever read a sentence that sounded awkward but couldn’t explain why, chances are it lacked parallelism.
Understanding parallel structure in sentences is essential for students, bloggers, business writers, and anyone who wants their content to sound polished and easy to read. In this guide, we’ll break down what parallel structure is, why it matters, and how to use it correctly without making your writing feel stiff or overly formal.
Let’s dive in.
What Is Parallel Structure in Sentences?
Parallel structure, also known as parallelism, means using the same grammatical form for similar ideas within a sentence. When elements in a sentence are connected by words like “and,” “or,” or “but,” they should follow the same pattern.
In simple terms, parallel structure keeps your writing consistent and balanced.
For example:
She enjoys reading, writing, and jogging.
All three items are in the same -ing form. That’s parallel structure.
Now compare it with this:
She enjoys reading, to write, and jogging.
This sentence feels off because the verb forms don’t match. “Reading” and “jogging” are gerunds, but “to write” is an infinitive. The lack of parallelism makes the sentence awkward.
Parallel structure in sentences improves clarity, flow, and readability. It helps your reader process information more easily, which is especially important in online content and SEO writing.
Why Parallel Structure Is Important in Writing
Parallel structure is not just a grammar rule for exams. It plays a key role in effective communication.
First, it improves readability. When your sentence structure is consistent, readers can follow your ideas without confusion. This is particularly important in blog posts, marketing copy, and educational content.
Second, it enhances clarity. When ideas are presented in the same grammatical form, they are clearly connected. The relationship between them becomes obvious.
Third, it strengthens persuasion. Many famous speeches use parallelism to create rhythm and emphasis. A well-known example comes from Martin Luther King Jr. in his famous speech at the Lincoln Memorial, where he repeated the phrase “I have a dream.” The repeated structure made his message powerful and memorable.
Parallel structure works the same way in everyday writing. It creates rhythm and gives your sentences a confident tone.
Common Situations Where Parallel Structure Is Needed
Parallel structure in sentences is most commonly used in lists, comparisons, and paired ideas.
When listing items, make sure each item follows the same grammatical form.
Correct example:
The course teaches students to analyze data, to write reports, and to present findings.
Here, each phrase begins with “to” followed by a verb. The structure is consistent.
When making comparisons, parallel structure is also necessary.
Correct example:
She prefers working remotely to commuting every day.
Both “working” and “commuting” are gerunds. The sentence feels natural and balanced.
Parallelism is also important with correlative conjunctions such as “either…or,” “not only…but also,” and “both…and.”
Correct example:
He is not only talented but also hardworking.
Both adjectives follow the same pattern. That balance keeps the sentence smooth.
Types of Parallel Structure in Sentences
Parallel structure can appear in different forms depending on the grammatical elements involved.
Parallel Structure with Verbs
One of the most common forms involves verbs.
Incorrect:
She likes to swim, biking, and to run.
Correct:
She likes to swim, to bike, and to run.
Or:
She likes swimming, biking, and running.
Both versions are correct because they maintain the same verb form throughout the sentence.
Parallel Structure with Adjectives
Parallelism also applies to descriptive words.
Incorrect:
The movie was exciting, emotional, and it was inspiring.
Correct:
The movie was exciting, emotional, and inspiring.
The corrected sentence removes the unnecessary shift in structure and keeps the adjectives consistent.
Parallel Structure with Clauses
When using clauses, maintaining parallel form is just as important.
Incorrect:
The manager said that the team should increase sales, improving customer service, and that marketing costs must be reduced.
Correct:
The manager said that the team should increase sales, improve customer service, and reduce marketing costs.
Now each action follows the same verb pattern, creating a cleaner and more professional sentence.
How to Identify Problems with Parallel Structure
Sometimes errors in parallel structure are easy to spot. Other times, they are subtle.
A good way to check is to look at the items joined by conjunctions like “and” or “or.” Ask yourself: Are these elements using the same grammatical form?
If not, revise them so they match.
Reading your sentence out loud also helps. Sentences without parallel structure often sound clumsy or unbalanced. If something feels awkward, check for consistency.
In SEO writing, especially for PBN content, smooth readability matters. Search engines evaluate user engagement signals, and readers are more likely to stay on a page that flows naturally. Clean sentence structure supports better user experience.
Parallel Structure and SEO Writing
You might wonder how parallel structure in sentences connects to SEO.
While search engines do not directly rank pages based on grammar rules, readability plays a huge role in content performance. When your writing is clear and structured, readers spend more time on the page. This reduces bounce rate and increases engagement.
Parallel structure also helps when writing headings and subheadings. Consistent formatting and phrasing make your article easier to scan. For example, using similar grammatical forms in section titles creates a sense of organization and professionalism.
In long-form articles, especially around 1000 words or more, maintaining parallelism keeps the tone consistent from beginning to end. This consistency builds trust with readers.
For PBN purposes, natural flow is crucial. Content that sounds robotic or inconsistent can raise red flags. Proper parallel structure makes the text feel human and thoughtfully written.
Tips to Master Parallel Structure in Sentences
Improving your use of parallel structure does not require advanced grammar knowledge. It simply requires attention and practice.
Start by identifying lists in your sentences. Ensure each item matches the others in form.
Pay attention to verb tense. If you begin with a past tense verb, keep the rest in past tense when listing related actions.
Be careful with phrases that mix gerunds and infinitives. Choose one structure and stick with it.
When using correlative conjunctions, double-check that both parts mirror each other grammatically.
Finally, revise and edit. Even experienced writers make mistakes. A quick review focused specifically on parallel structure can significantly improve the overall quality of your article.
Final Thoughts on Understanding Parallel Structure in Sentences
Understanding parallel structure in sentences is a simple but powerful way to improve your writing. It enhances clarity, strengthens your message, and creates a smoother reading experience.
Whether you are writing academic essays, blog posts, marketing copy, or PBN content, parallelism helps your sentences feel balanced and professional. It may seem like a small detail, but small details often make the biggest difference.

How to Use Conjunctions Like a Pro
How to Use Conjunctions Like a Pro – Conjunctions may seem like small, simple words, but they have a powerful role in shaping clear and engaging writing. Whether you’re crafting blog posts, website content, or authority articles for SEO purposes, mastering conjunctions can instantly improve your flow, readability, and overall professionalism.
If you’ve ever felt that your sentences sound choppy or disconnected, the problem might not be your ideas. It could simply be how you’re linking them together. When used correctly, conjunctions act as bridges, guiding readers smoothly from one thought to the next.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to use conjunctions like a pro, improve sentence variety, and create content that feels natural, polished, and easy to read.
Understanding What Conjunctions Really Do
At their core, conjunctions are connecting words. They join words, phrases, or clauses together. But beyond simple grammar rules, they influence tone, rhythm, and clarity.
Without conjunctions, writing becomes robotic. For example:
“I wanted to improve my writing. I studied grammar. I practiced daily.”
The ideas are clear, but the flow is stiff. Now look at this:
“I wanted to improve my writing, so I studied grammar and practiced daily.”
The meaning is the same, yet the second version feels smoother and more professional. That’s the power of conjunctions.
When creating SEO-focused content, especially for long-form articles, smooth transitions help keep readers engaged longer. That improves user experience signals, which indirectly supports better rankings.
The Three Main Types of Conjunctions
To use conjunctions effectively, you need to understand the three main categories: coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Each one serves a different purpose.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions connect elements of equal importance. These include words like and, but, or, so, for, nor, and yet.
They are perfect for combining related ideas without overcomplicating your sentence structure.
For example:
“You can focus on short content, or you can invest in long-form articles.”
Both parts of the sentence are balanced. Neither depends on the other to make sense.
In SEO writing, coordinating conjunctions help you expand ideas naturally. Instead of writing separate short sentences, you can combine them for better rhythm and improved readability.
However, avoid overusing “and.” Many writers rely too heavily on it, which makes writing feel repetitive. Try rotating between but, so, and yet to add variety.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions connect a dependent clause to an independent clause. Common examples include because, although, while, since, if, when, and even though.
These conjunctions add depth to your writing by showing relationships such as cause, contrast, condition, or time.
For example:
“Because content quality matters, you should always edit carefully.”
The first part cannot stand alone. It depends on the second clause to complete the meaning.
Subordinating conjunctions are especially valuable in SEO articles because they allow you to explain concepts more clearly. Instead of listing facts, you can demonstrate reasoning.
Compare this:
“Content marketing works. It builds trust.”
Now with a subordinating conjunction:
“Content marketing works because it builds trust.”
The second sentence feels stronger and more convincing. That subtle difference improves the authority of your content.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions work in pairs. Examples include both…and, either…or, neither…nor, and not only…but also.
They emphasize balance between two ideas.
For instance:
“Not only does strong grammar improve clarity, but it also enhances credibility.”
This structure creates emphasis and adds a persuasive tone. It’s particularly useful when writing sales-focused or conversion-driven content.
Be careful to maintain parallel structure when using correlative conjunctions. The grammatical form after each part of the pair should match. If it doesn’t, your sentence will sound awkward.
How Conjunctions Improve SEO Content
Using conjunctions properly isn’t just about grammar. It directly affects readability, engagement, and content quality.
Search engines prioritize content that satisfies user intent. If your writing feels disjointed, readers leave quickly. That increases bounce rate and reduces time on page.
Conjunctions help by:
Creating smoother transitions between ideas
Reducing repetitive sentence structures
Making complex topics easier to understand
Encouraging longer, more natural sentences
When readers can follow your logic effortlessly, they stay longer. And when they stay longer, your content performs better.
In PBN articles especially, natural flow is critical. Overly mechanical writing can appear low quality. Strategic use of conjunctions helps your article feel authentic and human.
Avoiding Common Conjunction Mistakes
Even experienced writers misuse conjunctions. Here are a few common pitfalls to avoid.
One mistake is creating comma splices. This happens when two independent clauses are joined by a comma without a coordinating conjunction.
Incorrect:
“I updated the website, it started ranking better.”
Correct:
“I updated the website, and it started ranking better.”
Another mistake is overloading sentences with too many conjunctions.
“I wanted to improve traffic and increase conversions and build authority and grow revenue.”
While technically correct, the sentence feels heavy. Breaking it up slightly improves clarity:
“I wanted to improve traffic, increase conversions, and build authority so I could grow revenue.”
Balance is key. Conjunctions should enhance readability, not overwhelm it.
Creating Natural Flow in Long-Form Articles
Long-form content requires careful sentence variation. If every sentence follows the same pattern, readers lose interest.
Try mixing short, punchy sentences with longer, connected ones.
For example:
“SEO takes time. Results rarely happen overnight. However, consistent effort eventually pays off.”
Here, “however” acts as a transition, connecting ideas smoothly without making the structure repetitive.
You can also begin sentences with conjunctions occasionally. Despite what some teachers once insisted, starting a sentence with “and” or “but” is perfectly acceptable in modern writing when used intentionally.
For example:
“But strong backlinks alone are not enough.”
Used sparingly, this technique adds rhythm and conversational tone.
Using Conjunctions to Strengthen Authority
Professional writing often relies on logical progression. Conjunctions make arguments clearer and more persuasive.
Consider this example:
“Many websites publish content regularly. Few focus on quality.”
Now strengthened:
“Although many websites publish content regularly, few focus on quality.”
The second version shows contrast more clearly. It guides the reader toward your point instead of leaving them to interpret the connection.
This is particularly useful in educational or strategy-based articles, where you need to guide readers step by step.
Practice Makes Perfect
Like any writing skill, mastering conjunctions requires practice. Start by reviewing your older articles. Look for areas where sentences feel abrupt or disconnected.
Ask yourself:
Can two short sentences be combined?
Is there a clearer way to show cause or contrast?
Am I overusing one specific conjunction?
Editing with conjunctions in mind often improves an article instantly without changing its core message.
Final Thoughts
Conjunctions may be small words, but they shape the entire reading experience. They connect ideas, clarify meaning, and create a natural flow that keeps readers engaged.
If you want to write like a pro, don’t just focus on keywords or word count. Focus on how your sentences interact with each other. Strong transitions and logical connections make your content more persuasive, more readable, and ultimately more effective.

Learning English Grammar Effectively in Indonesia
Learning English grammar effectively in Indonesia – has become more important than ever. As globalization continues to grow, English is no longer just a school subject. It is a key skill for higher education, career opportunities, digital communication, and even entrepreneurship. From university students in Jakarta to young professionals in Surabaya, the demand for strong English grammar skills keeps increasing every year.
Indonesia has made major efforts to improve English education. The Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology, known as Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, dan Teknologi, includes English as a core subject in many schools. However, many learners still struggle with grammar accuracy, sentence structure, and confidence in writing and speaking.
This article explores how to learn English grammar effectively in Indonesia using practical strategies, local context, and consistent habits. If you want to improve your English grammar naturally and efficiently, keep reading.
Why English Grammar Is Important for Indonesian Learners
English grammar forms the foundation of clear communication. Without proper grammar, ideas can easily be misunderstood. For Indonesian learners, grammar can be challenging because Bahasa Indonesia has a very different structure compared to English.
In Bahasa Indonesia, verbs do not change based on time. In English, verb tenses are essential. For example, “I eat,” “I ate,” and “I have eaten” all express different time references. This difference often creates confusion for Indonesian students when learning English grammar.
Strong grammar skills help learners:
Improve academic writing
Prepare for international tests
Communicate professionally
Build confidence in speaking
Many Indonesian students aim to study abroad in countries like Australia, United Kingdom, or United States. For this reason, mastering English grammar becomes a long-term investment.
Common Grammar Challenges in Indonesia
There are several grammar areas that Indonesian learners commonly struggle with.
First is verb tense consistency. Because Bahasa Indonesia does not use tense changes, learners often forget to adjust verbs when talking about past or future events.
Second is subject-verb agreement. English requires “She goes” instead of “She go.” This small difference may seem simple, but it frequently appears in writing mistakes.
Third is the use of articles such as “a,” “an,” and “the.” Since Bahasa Indonesia does not use articles in the same way, learners may omit them or use them incorrectly.
Understanding these challenges is the first step toward learning English grammar effectively in Indonesia.
Effective Strategies to Learn English Grammar in Indonesia
Improving grammar does not require complicated methods. The key is consistency and smart practice. Here are proven strategies that work well for Indonesian learners.
Build a Strong Foundation First
Before moving to advanced grammar topics, make sure you understand the basics. Focus on sentence structure, basic tenses, pronouns, and prepositions. Many students try to learn complex grammar without mastering simple present or simple past tense.
Use reliable grammar books or structured courses. If possible, follow a curriculum that gradually increases in difficulty. A clear learning path prevents confusion and frustration.
Practice Through Daily Writing
Writing is one of the most effective ways to improve English grammar. Start with short daily journals. Write about your activities, plans, or opinions. Keep it simple but consistent.
After writing, check your grammar. You can compare your sentences with grammar references or ask a teacher for feedback. Over time, you will notice patterns in your mistakes and improve naturally.
In cities like Jakarta and Bandung, many learners join English communities to practice writing and speaking together. This collaborative environment helps reinforce grammar in real communication.
Learn Grammar in Context
Memorizing rules alone is not enough. Grammar should be learned in context. Read English articles, short stories, or news. Pay attention to how sentences are structured.
Watching English movies or series can also help. Listen carefully to how native speakers use tenses and expressions. Even though this method focuses more on listening, it strengthens your understanding of grammar patterns.
Try to notice how questions are formed, how conditional sentences are used, and how connectors link ideas together. This natural exposure makes grammar learning less stressful.
Take Advantage of Online Resources
Indonesia has rapidly growing internet access. This creates many opportunities for online English learning. You can find grammar exercises, quizzes, and video explanations easily.
Online courses allow learners from smaller cities to access the same quality of materials as those in major cities. Flexibility is a big advantage because students can study at their own pace.
However, avoid jumping between too many resources. Choose one or two reliable platforms and focus on completing them consistently.
The Role of English Courses in Indonesia
Formal education sometimes provides limited time for deep grammar practice. Because of this, many students enroll in private English courses.
Institutions such as EF Education First and British Council have programs available in Indonesia. These institutions offer structured grammar lessons combined with speaking and writing practice.
Local English courses also play an important role. Many neighborhood learning centers provide affordable options for students. The key is not the brand name, but the quality of teaching and consistent practice.
If you choose a course, make sure it includes regular feedback. Grammar improvement requires correction and guidance.
Creating a Sustainable Grammar Learning Habit
Learning English grammar effectively in Indonesia is not about studying for one week and expecting instant results. It is about building sustainable habits.
Set a realistic goal. For example, learn one grammar topic per week. Practice it in writing and speaking. Review it at the end of the week before moving to a new topic.
Consistency is more important than intensity. Studying 20 minutes every day is more effective than studying three hours once a week.
Combine Grammar with Speaking Practice
Many Indonesian learners understand grammar rules but hesitate to speak. They are afraid of making mistakes. In reality, making mistakes is part of learning.
Try to join English-speaking communities or language exchange programs. Practice forming sentences using the grammar you recently studied. This reinforces your understanding and builds confidence.
You can also practice by talking to yourself in English about your daily routine. It may feel unusual at first, but it helps you think in English and apply grammar automatically.
Staying Motivated While Learning English Grammar
Motivation can go up and down. To stay motivated, remind yourself why you are learning English. Maybe you want to work for an international company, study abroad, or expand your business network.
Celebrate small progress. If you can write a paragraph without major grammar mistakes, that is an achievement. If you can explain past events correctly using past tense, that is progress.
Learning English grammar effectively in Indonesia is absolutely possible. With the right strategies, consistent practice, and supportive environment, anyone can improve step by step.

Grammar in the Courts of Medieval Kingdoms

English grammar made easy for daily use
English grammar made easy for daily use – Learning English grammar often feels harder than it should be. Many learners think grammar is all about memorizing complicated rules, long formulas, and confusing terms. In reality, grammar is simply a tool to help you communicate clearly in everyday situations. When you focus on daily use, English grammar becomes much easier and more practical.
This article will help you understand English grammar in a simple way, especially for daily conversations, work communication, and casual writing. You don’t need to sound like a native speaker or a grammar expert. You only need grammar that works in real life.
Why English Grammar Matters in Daily Life
Grammar is not about perfection. It is about clarity. When you use basic grammar correctly, people understand you faster and respond better. In daily situations like chatting with friends, sending emails, or speaking at work, simple grammar is more than enough.
Many English learners stop practicing because they feel grammar is too strict. The truth is, native speakers often use simple structures and even make small mistakes. What matters is that the message is clear and natural.
By learning grammar for daily use, you can speak with more confidence and less fear of making mistakes.
Understanding Grammar as a Pattern, Not a Rulebook
One common mistake is treating English grammar like math. Grammar works better when you see it as patterns that repeat in daily conversations.
For example, most daily English sentences follow a simple pattern. Someone does something, or something happens. Once you get used to these patterns, forming sentences becomes automatic.
Instead of memorizing grammar rules, try to notice how people actually speak. Watch videos, read simple articles, or listen to podcasts. You will see the same sentence structures used again and again.
Simple Tenses for Everyday Communication
You don’t need all twelve tenses to survive daily English. In most conversations, only a few are used regularly.
The present simple tense is extremely common. People use it to talk about routines, habits, and facts. Sentences like “I work from home” or “She likes coffee” are everywhere.
The present continuous tense is used when something is happening now or temporarily. You hear it in sentences like “I’m working right now” or “They’re watching a movie.”
Past simple tense is enough to talk about things that already happened. You don’t need complex past forms for daily use. “I went there yesterday” or “We finished the meeting” is perfectly fine.
Future ideas are often expressed with simple forms too. Many people use “will” or “going to” without thinking too much about the difference.
Making Sentences Sound Natural Without Overthinking
One of the biggest challenges in learning English grammar is overthinking. Learners often pause too long because they are afraid of making mistakes. This breaks the flow of conversation.
To sound more natural, keep your sentences short and direct. Daily English is not about long, complex sentences. It is about clear ideas.
Instead of trying to sound advanced, focus on sounding understandable. Simple grammar with correct word order sounds better than complicated grammar used incorrectly.
Word Order in Daily English
English word order is quite stable. Most sentences follow the same structure. When you stick to this pattern, your grammar instantly improves.
Questions in daily English also follow common patterns. You don’t need to create perfect grammar questions every time. As long as your question is clear, people will understand.
Negative sentences are also simple. Using basic negative forms is enough for daily communication. You don’t need fancy grammar to say what you don’t want or don’t like.
Common Grammar Mistakes That Don’t Really Matter
Many learners worry too much about small grammar mistakes. In real life, people care more about meaning than grammar accuracy.
For example, missing an article or using the wrong preposition usually doesn’t stop communication. Native speakers make these mistakes too, especially in casual speech.
Instead of trying to fix everything at once, focus on the mistakes that change meaning. If people understand you, your grammar is already doing its job.
Spoken English vs Written English Grammar
Spoken English grammar is more flexible than written grammar. In daily conversations, people shorten sentences, skip words, and use informal structures.
Written English, especially in emails or messages, is still simple but slightly more organized. You don’t need perfect academic grammar for daily writing. Clear and polite sentences are enough.
Understanding this difference helps you relax and use grammar more naturally.
Learning Grammar Through Daily Practice
The best way to learn English grammar is not through textbooks alone. Daily exposure and practice make grammar stick.
Try using English in small ways every day. Write short messages, think in English, or describe your day using simple sentences. Over time, grammar becomes a habit, not a struggle.
Reading simple content also helps. Articles, blogs, and short stories written in natural English show you how grammar is used in real contexts.
Listening is just as important. When you hear grammar used naturally, your brain starts copying the patterns without conscious effort.
Building Confidence with Simple Grammar
Confidence is more important than perfect grammar. When you stop worrying about being perfect, you speak more freely and improve faster.
English grammar made easy for daily use is about practicality. You don’t need advanced grammar to live, work, or socialize in English. You need grammar that supports communication, not blocks it.
Start with simple structures, repeat them often, and trust the process. Grammar will slowly become something you use automatically.
Final Thoughts on English Grammar Made Easy
English grammar does not have to be scary or complicated. When you focus on daily use, grammar becomes simple, logical, and useful.
Forget about memorizing every rule. Learn patterns, practice daily, and allow yourself to make mistakes. That is how real communication works.
With the right mindset and consistent exposure, English grammar becomes less about rules and more about expression. And that is when English truly becomes easy.
British vs American Grammar Differences
British vs American Grammar Differences – English is a global language, but it is far from uniform. Two of its most influential varieties, British English and American English, share the same roots yet differ in many subtle and not-so-subtle ways. For learners, writers, and website owners, understanding British vs American grammar differences is essential for clarity, consistency, and credibility.
These differences do not usually block communication, but they can affect how professional or natural your writing sounds. In SEO-focused content, especially for niche sites and PBNs, consistency in grammar style helps search engines and readers trust your content more.
This article explores the most important grammar differences between British and American English in a simple, practical way.
Why British and American English Are Not Exactly the Same
British English developed earlier and was shaped by historical usage in the United Kingdom. American English evolved after English arrived in North America, influenced by immigration, local culture, and language simplification over time.
As a result, American English tends to favor efficiency and regularity, while British English often preserves traditional forms. These distinctions appear clearly in grammar, spelling, and sentence construction.
Understanding which version you are using matters, especially when your audience is primarily from the US or the UK.
Verb Forms and Tense Usage
Present Perfect vs Simple Past
One of the most noticeable grammar differences lies in how the present perfect tense is used.
British English uses the present perfect more frequently to describe recent actions or experiences with present relevance. For example, a British speaker might say, “I have just finished my work.”
American English often prefers the simple past in the same situation, saying, “I just finished my work.”
Both forms are grammatically correct, but mixing them within the same article can feel inconsistent. For SEO writing, choosing one style and sticking with it is highly recommended.
Past Participles and Irregular Verbs
Some verbs have different past participle forms in British and American English. In British English, “learnt,” “dreamt,” and “burnt” are commonly used. American English favors “learned,” “dreamed,” and “burned.”
Neither is wrong. However, American English generally prefers regular verb endings, while British English is more flexible with irregular forms.
Collective Nouns and Subject Agreement
Collective nouns such as team, staff, government, or family behave differently in the two varieties.
British English often treats collective nouns as plural, especially when emphasizing individuals within the group. For example, “The team are playing well today.”
American English almost always treats collective nouns as singular, focusing on the group as a unit. The American version would be, “The team is playing well today.”
This difference affects verb agreement and pronoun usage. Mixing styles can make sentences sound awkward or unpolished.
Prepositions and Grammar Structures
Differences in Preposition Usage
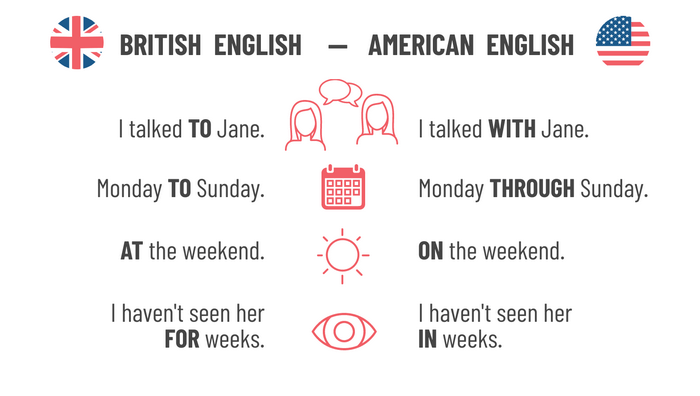
Prepositions are a common source of confusion. British and American English use different prepositions in many everyday expressions.
British English speakers say “at the weekend,” while American English uses “on the weekend.” Another example is “different to” or “different from” in British English, compared to the American preference for “different from” or “different than.”
These small differences may seem minor, but they add up. Search engines and native readers often subconsciously notice them.
Omission of Prepositions
American English sometimes omits prepositions that British English retains. For instance, Americans say “Monday through Friday,” while British speakers usually say “Monday to Friday.”
Again, consistency is more important than choosing one as “better.”
Use of Articles
Articles like “the,” “a,” and “an” are used slightly differently across the two varieties.
British English often includes “the” in phrases where American English drops it. A common example is “in hospital” versus “in the hospital.” British English focuses on the activity or condition, while American English refers more to the physical place.
The same pattern appears with “at university” and “at the university.”
Understanding this difference helps writers avoid sounding unnatural to their target audience.
Auxiliary Verbs and Modal Usage
Shall vs Will
“Shall” is more common in British English, especially in formal writing or polite suggestions. For example, “Shall we begin?”
In American English, “shall” is rare outside of legal or very formal contexts. Americans almost always use “will,” as in “Will we begin?”
If your content is aimed at a US audience, frequent use of “shall” can feel outdated or overly formal.
Need and Have Got
British English commonly uses “have got” to express possession, such as “I have got a new phone.” American English prefers the simpler “I have a new phone.”
Similarly, British English sometimes uses “needn’t,” while American English uses “don’t need to.”
Spelling Differences That Affect Grammar Perception
Although spelling is not grammar itself, it strongly influences how grammar is perceived.
British English uses spellings like “organise,” “colour,” and “centre.” American English prefers “organize,” “color,” and “center.”
Mixing spelling systems within the same article is one of the fastest ways to lose credibility, especially for SEO-focused websites. Choose one standard and apply it consistently across all pages.
Punctuation and Quotation Marks
British and American English differ in punctuation rules, particularly with quotation marks.
British English often places punctuation outside quotation marks unless it is part of the quoted material. American English almost always places commas and periods inside quotation marks.
For example, American English writes: She said, “It’s done.”
British English may write: She said, “It’s done”.
While subtle, these details matter for professional-level writing.
Which Grammar Style Should You Use for SEO?
From an SEO perspective, American English is generally more dominant due to the size of the US market and search volume. However, British English is more appropriate if your audience is based in the UK, Australia, or other Commonwealth countries.
The key rule is not which version you choose, but how consistently you apply it. Search engines value clarity, coherence, and user experience. Mixing British and American grammar can reduce readability and trust.
For PBN content, clean grammar, natural flow, and a clear language identity help pages look more authentic and less automated.
Final Thoughts on British vs American Grammar Differences
British and American English are two sides of the same coin. Their grammar differences reflect history, culture, and evolving language habits rather than strict right or wrong rules.
By understanding these distinctions, writers can produce more natural, targeted, and effective content. Whether you choose British or American grammar, consistency is your strongest asset.
For SEO and PBN purposes, well-structured writing with a clear grammatical identity not only improves rankings but also builds long-term credibility with readers and search engines alike.

Grammar Rules That Change Meaning Into Horror
Grammar Rules That Change Meaning Into Horror – Grammar is often thought of as the backbone of good writing, a set of rules to keep our sentences clear and precise. But what happens when these rules are broken—or bent just slightly? Suddenly, your words can shift from being clear to downright horrifying, and not in the fun, spooky way you might expect. In this article, we’ll explore how small grammar mistakes or twists can change meaning drastically, sometimes creating unintended terror in your writing.
The Power of Commas: Pause for Effect—or Panic
Commas are deceptively small but can wield immense power over meaning. A misplaced comma can turn a friendly sentence into something that sounds eerie or sinister. Consider the difference between these two sentences:
“Let’s eat, Grandma.”
“Let’s eat Grandma.”
One comma transforms a loving invitation into a horrifying act of cannibalism. This is a classic example, but the point is clear: punctuation isn’t just about following rules—it’s about preventing unintended meaning.
Commas can also create suspense or unease in longer sentences. For instance, in horror writing, a well-placed pause can make the reader hesitate, building tension. In everyday writing, however, misuse can confuse or shock your audience in ways you didn’t intend.
Subject-Verb Agreement: When the Sentence Rebels
Subject-verb agreement is another rule that seems basic, yet breaking it can make your sentences unexpectedly creepy or confusing. Imagine a simple description gone wrong:
“The shadows moves along the walls.”
Here, the plural “shadows” mismatched with “moves” gives an unnatural, almost ghostly quality to the sentence. The mind unconsciously senses that something is off, which can create a subtle unease in the reader. In horror, this can actually be used deliberately to evoke discomfort, but in standard writing, it’s usually a source of accidental strangeness.
Pronouns: Ambiguity That Haunts
Pronouns are meant to clarify who or what you’re talking about. But when misused, they can turn clarity into confusion—or horror. Consider:
“She looked at her in the dark.”
Who is “she”? Who is “her”? The ambiguity can create a sense of dread, as if a sinister presence is lurking just beyond comprehension. This isn’t just a stylistic quirk; it’s a natural byproduct of sloppy grammar. In horror writing, authors might exploit this to leave readers unsettled, but in everyday writing, pronoun misuse often leads to confusion or misinterpretation.
Misplaced Modifiers: Accidental Monsters
Modifiers describe or limit other words, but when misplaced, they can produce sentences that sound unintentionally monstrous. For example:
“Covered in blood, the detective examined the scene.”
This sentence seems clear, but imagine if we misplace the modifier:
“The detective examined the scene covered in blood.”
Suddenly, the detective is the one covered in blood, creating an unintended and grisly image. Misplaced modifiers are a subtle way grammar can transform meaning into something horrific without the writer intending it.
Tense Confusion: When Time Itself Becomes Creepy
Verb tense is meant to orient the reader in time. When used inconsistently, it can make events feel disjointed or even surreal. For instance:
“She walks into the house and found the door open.”
The sudden shift from present to past creates a jarring effect. In horror writing, this could simulate disorientation, making the reader feel unsteady. In non-fiction or casual writing, it simply feels wrong and can turn a simple story into something unintentionally unsettling.
Apostrophes: Tiny Marks, Big Consequences
Apostrophes are tiny but mighty. They can completely change meaning when misplaced. For example:
“The ghost’s whispers were terrifying.” versus “The ghosts’ whispers were terrifying.”
One little apostrophe alters whether there is one ghost or many. Even more perilous is:
“Its cold grip was everywhere.” versus “It’s cold grip was everywhere.”
A misplaced apostrophe can break immersion or confuse the reader, sometimes creating a subtle, creeping sense of wrongness that’s perfect for horror—or frustrating for everyday writing.
Word Choice and Homophones: Horror in Disguise
Homophones—words that sound the same but have different meanings—are infamous for creating accidental horror. For example:
“The knight approached the haunted hall.” versus “The night approached the haunted hall.”
A single misused word can shift your scene from a medieval adventure to a potentially terrifying, uncanny scenario. For PBN sites and other content-driven platforms, paying attention to these small errors ensures your text communicates exactly what you intend—without accidental frights.
How Grammar Can Be Used Deliberately in Horror
Interestingly, many of the “horrors” we’ve discussed aren’t always mistakes. Skilled writers can intentionally bend grammar rules to evoke unease. Fragmented sentences, mismatched tenses, ambiguous pronouns—all of these can make readers uncomfortable in the right context. For instance, horror authors often use short, choppy sentences to simulate panic, while shifting tenses or ambiguous references keep readers on edge.
For SEO-focused PBN content, it’s less about scaring readers and more about understanding how grammar impacts meaning. But for creative writing, these “mistakes” can become tools to craft tension, suspense, or outright fear.
Conclusion: Small Rules, Big Impact
Grammar isn’t just about following rules—it’s about controlling meaning. Misplaced commas, mismatched verbs, ambiguous pronouns, and other small errors can turn an ordinary sentence into something unintentionally horrifying. Understanding these rules helps you avoid confusion in your writing, and in some contexts, allows you to harness grammar itself as a tool for creative effect.
Whether you’re writing for PBN sites, blogging, or crafting fiction, paying attention to these subtleties ensures your message lands as intended—and prevents accidental nightmares on the page. Grammar may seem boring, but as we’ve seen, even the smallest misstep can have a surprisingly dramatic effect.

A Practical Guide to English Grammar for Everyday Writing
A Practical Guide to English Grammar for Everyday Writing – Writing in English can feel challenging, especially when it comes to grammar. Even experienced writers sometimes struggle with sentence structure, punctuation, or word choice. The good news is that you don’t need to memorize every rule to write clearly and effectively. Understanding the essentials of grammar and applying them consistently can make your everyday writing more confident and professional.
This guide is designed to help you navigate English grammar in practical ways, focusing on the aspects that matter most for daily communication, emails, social media posts, reports, and personal writing.
Why Grammar Matters in Everyday Writing
Grammar is often seen as a set of strict rules, but at its core, it’s a tool for communication. Good grammar helps your reader understand your message without confusion. In everyday writing, proper grammar can make a difference in how you are perceived. Clear sentences, correct punctuation, and smooth word flow create a sense of professionalism and attention to detail.
On the other hand, small mistakes can distract readers or even change the meaning of your message. Mastering grammar for everyday writing isn’t about perfection—it’s about clarity, consistency, and ease of reading.
Common Grammar Challenges
Sentence Structure and Word Order
One of the most common difficulties in English writing is sentence structure. English generally follows a Subject-Verb-Object order. For example: “She reads a book.” This seems simple, but complexity increases when adding modifiers, clauses, or extra information.
To improve clarity:
-
Keep your subject and verb close together.
-
Avoid long chains of clauses unless necessary.
-
Break long sentences into two for readability.
Verb Tenses and Consistency
Verb tenses indicate time, but using them inconsistently can confuse readers. A typical error is mixing past and present tenses within the same paragraph. For example: “I go to the store yesterday and bought some fruit.” The sentence should be: “I went to the store yesterday and bought some fruit.”
For everyday writing, focus on using tenses that match the timeline of events and be consistent throughout your text.
Articles and Determiners
Articles such as “a,” “an,” and “the” can be tricky for many learners. They are small words but significantly impact clarity.
-
Use “a” or “an” for general, non-specific items: “I need a pen.”
-
Use “the” for specific items already mentioned or known: “I found the pen you lost.”
The key is reading and exposure. The more you see articles used correctly, the more natural their use becomes.
Tips for Everyday Writing
Keep Sentences Clear and Direct
Everyday writing benefits from simplicity. Avoid overcomplicating sentences with too many ideas. Each sentence should ideally express one main thought.
For example, instead of writing: “I was thinking that maybe we could, if you have time, discuss the project plan tomorrow,”
you can simplify it to: “If you have time, let’s discuss the project plan tomorrow.”
Clear sentences improve readability and reduce grammar mistakes.
Read and Imitate Good Writing
One of the best ways to internalize grammar is to read well-written material. Look for articles, blogs, or books with strong grammar and sentence flow.
When you notice a sentence you like, analyze it:
-
How is the subject positioned?
-
Which verb tense is used?
-
How are modifiers and clauses arranged?
Over time, you’ll naturally adopt these patterns in your own writing.
Use Punctuation Wisely
Punctuation is the signpost of your writing. Commas, periods, colons, and semicolons help the reader navigate your sentences. Incorrect punctuation can obscure meaning.
A few practical rules for everyday writing:
-
Use periods to separate complete thoughts.
-
Use commas to divide clauses or list items.
-
Avoid overusing semicolons unless you are confident with them.
Simple punctuation habits go a long way in improving clarity.
Improving Grammar Through Practice
Daily Writing Habits
The most effective way to improve grammar is through consistent writing. Journaling, short essays, emails, or even social media posts can help. The goal is to apply grammar actively rather than passively memorizing rules.
Start small: write a paragraph each day focusing on a specific grammar point, like verb tenses or sentence structure. Gradually, these habits build a solid foundation.
Review and Revise
Editing your writing is as important as writing itself. First drafts often contain small grammar errors that are easy to fix on revision.
When reviewing:
-
Read your text aloud to catch awkward phrasing.
-
Check for verb tense consistency.
-
Ensure punctuation and articles are used correctly.
Revision turns raw ideas into polished, professional writing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced writers fall into common traps. Some everyday mistakes include:
-
Mixing singular and plural subjects: “The team are ready” vs. “The team is ready.”
-
Using incorrect verb forms: “He run every day” instead of “He runs every day.”
-
Confusing words that sound alike: “there,” “their,” and “they’re.”
Being aware of these patterns allows you to catch errors before they become habits.
The Role of Grammar in Professional Writing
Grammar matters most when your writing represents you professionally. Emails, reports, proposals, and presentations benefit from correct grammar because it conveys competence and attention to detail.
Even small improvements in sentence clarity and word choice can significantly impact how your writing is received. Well-structured sentences create authority, while sloppy grammar can distract or mislead the reader.
Making Grammar Work for You
Grammar is not a set of restrictions; it is a toolkit. Once you understand the rules and common patterns, you can use them to make your writing stronger and more expressive.
Focus on:
-
Clarity over complexity.
-
Consistency over memorization of every exception.
-
Regular practice and revision to reinforce skills.
When grammar becomes a natural part of your writing process, everyday writing no longer feels daunting. Instead, it becomes a way to communicate clearly, creatively, and confidently.
Final Thoughts
English grammar for everyday writing doesn’t have to be intimidating. By focusing on practical rules, clear sentence structures, and consistent practice, anyone can improve their writing.
The goal is not to achieve perfection but to make your ideas understandable and engaging. Grammar is a tool, not a burden, and using it effectively enhances every piece of writing you create.
With patience, reading, and daily practice, everyday writing can become both effortless and enjoyable, making your English communication more powerful and professional.

Why English Grammar Feels Hard and How to Master It Easily

Simple English Grammar Rules People Often Get Wrong
Simple English Grammar Rules People Often Get Wrong – English grammar looks simple on the surface, but many learners and even native speakers still make the same mistakes again and again. These errors may seem small, yet they can affect clarity, professionalism, and credibility, especially in writing.
In this article, we will discuss simple English grammar rules people often get wrong, explain why they happen, and show how to fix them naturally. This guide is written in a friendly tone, easy to understand, and practical for everyday use.
Subject and Verb Agreement Confusion
One of the most common grammar problems in English is subject and verb agreement. This rule sounds basic, but it often becomes tricky in longer sentences.
A singular subject must use a singular verb, while a plural subject must use a plural verb. Problems usually appear when other words come between the subject and the verb.
For example, many people write “The list of items are on the table.” The real subject is “list,” not “items,” so the correct sentence is “The list of items is on the table.”
Collective Nouns and Agreement
Collective nouns such as team, family, or group also confuse writers. In American English, these words are usually treated as singular. So, “The team is winning” is considered correct, even though the team includes many people.
Understanding what the true subject is will help you avoid this mistake in most cases.
Using “Your” and “You’re” Incorrectly
This is a classic error that still appears everywhere, especially online. “Your” shows possession, while “you’re” is a contraction of “you are.”
When people write quickly, they often forget the difference. A simple trick is to replace “you’re” with “you are.” If the sentence still makes sense, then “you’re” is correct.
For example, “You’re going to love your new job” uses both forms correctly. Mixing them up can make writing look careless, even if the message is clear.
Confusion Between “Its” and “It’s”
Another small apostrophe mistake that causes big confusion is between “its” and “it’s.” “It’s” means “it is” or “it has,” while “its” shows possession.
A sentence like “The company changed it’s policy” is incorrect. The correct form is “The company changed its policy.”
This mistake is common because most possessive nouns in English use apostrophes, but “its” is an exception.
Run-On Sentences and Comma Splices
Run-on sentences happen when two complete ideas are joined without proper punctuation. Comma splices are a specific type of run-on sentence where a comma is used instead of a period or conjunction.
For example, “I finished the report, I sent it to my manager” is incorrect. These are two independent sentences.
You can fix this by adding a conjunction, changing the comma to a period, or restructuring the sentence. Simple fixes like these make writing much easier to read.
Overusing or Misusing Commas
Commas are helpful, but too many commas can be just as confusing as too few. Many writers place commas where they feel a pause, not where grammar rules require them.
A common mistake is putting a comma between a subject and verb, such as “My brother, works in marketing.” This comma should not be there.
Commas After Introductory Phrases
On the other hand, commas are often missing after introductory phrases. For example, “After finishing the project we took a break” should include a comma after “project.”
Learning basic comma rules improves sentence flow and prevents misunderstandings.
Mixing Up “Then” and “Than”
“Then” relates to time or sequence, while “than” is used for comparisons. Even though the difference is simple, many people still confuse them.
For example, “She is taller then her sister” is incorrect. The correct sentence is “She is taller than her sister.”
This mistake often happens because both words sound similar when spoken quickly.
Incorrect Use of Articles: A, An, and The
Articles are a major challenge for non-native English speakers. English uses “a” and “an” for general nouns and “the” for specific ones.
A common error is saying “She is the doctor” when the speaker means any doctor, not a specific one. In that case, “She is a doctor” is more natural.
Understanding whether a noun is general or specific helps you choose the right article.
Confusion Between Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Some nouns in English cannot be counted individually, such as information, advice, and furniture. These words do not have plural forms, but many learners try to add “s” to them.
For example, “many informations” is incorrect. The correct phrase is “a lot of information.”
This mistake often comes from translating directly from another language.
Using the Wrong Prepositions
Prepositions are small words, but they cause big problems. Common examples include confusing “in,” “on,” and “at,” or “for” and “since.”
There is no single rule that works for all situations, which makes prepositions difficult. The best way to learn them is through exposure and practice, not memorization alone.
Reading English content regularly helps you notice which prepositions sound natural in different contexts.
Mixing Past Simple and Present Perfect
Many English learners struggle with the difference between past simple and present perfect. Past simple refers to a finished time, while present perfect connects the past to the present.
For example, “I have seen him yesterday” is incorrect. “Yesterday” is a finished time, so the correct sentence is “I saw him yesterday.”
This rule becomes clearer when you focus on time expressions.
Conclusion
Simple English grammar rules are often overlooked because they seem obvious. However, these small mistakes appear frequently in everyday writing and speech. By understanding why they happen and paying attention to common patterns, you can improve your English naturally.
Good grammar does not mean perfect grammar. It means clear communication. With consistent reading, writing, and awareness, avoiding these common grammar mistakes becomes much easier over time.

Practical English Grammar for Daily Writing and Speaking
Practical English Grammar for Daily Writing and Speaking – Mastering English grammar is often seen as a daunting task, but in reality, understanding practical grammar rules can make daily writing and speaking much easier. Whether you are writing emails, chatting with friends, or giving presentations, a solid grasp of grammar helps you communicate clearly and confidently. This article explores practical English grammar tips that you can apply every day to improve both your writing and speaking skills.
Why Practical Grammar Matters
Grammar is more than just rules; it is the framework that ensures your ideas are understood. Misplaced words or incorrect tenses can confuse your reader or listener, even if your vocabulary is strong. Practical grammar focuses on what is most useful for daily communication rather than memorizing every rule in a textbook.
For example, using the correct tense in a short story or during a conversation about yesterday’s events prevents misunderstandings. Similarly, understanding sentence structure helps you express thoughts logically and fluently.
Everyday Benefits of Good Grammar
Using proper grammar in daily life has tangible benefits. It enhances clarity, making your writing easier to read and your speech easier to follow. For professionals, it creates a positive impression, showing attention to detail and effective communication skills. For students, it supports academic success by improving essays, reports, and presentations.
Most importantly, grammar provides confidence. When you know your sentences are correct, you can focus on your ideas rather than worrying about mistakes.
Common Grammar Challenges
Many English learners face similar challenges, especially when it comes to daily communication. Recognizing these challenges helps in addressing them effectively.
Tense Confusion
Tenses are one of the most common difficulties. Choosing between past, present, and future tenses can be tricky, especially in casual conversation where time references can shift quickly. Practical grammar focuses on using the most common tenses correctly. For example, simple past is often enough when telling a story about yesterday, while present continuous works well for ongoing actions.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Matching the subject with the correct verb form is another frequent problem. Errors like “He go to school” instead of “He goes to school” can distract the listener or reader. Daily practice with common verbs and subject forms improves accuracy and fluency.
Sentence Structure and Word Order
English word order can differ from other languages. Mistakes in sentence structure can make statements unclear. Learning the basic order—subject, verb, object—helps construct sentences that sound natural in both writing and speaking.
Practical Grammar Tips for Writing
Writing clearly and correctly requires more than just spelling and vocabulary. Applying practical grammar rules ensures your messages are easy to read and understand.
Use Simple Sentences
Simple sentences are often more effective than complex ones. Instead of stacking multiple clauses, focus on one idea per sentence. This improves readability and reduces mistakes. For instance, “I finished my homework. Then I watched a movie” is clearer than “After finishing my homework, I watched a movie, which was very interesting and relaxing.”
Consistent Tense Usage
Maintaining the same tense within a paragraph prevents confusion. When writing about past events, stick to past tense unless a shift is necessary. Consistency keeps your reader oriented in time and makes your writing flow naturally.
Correct Punctuation
Punctuation is a small but powerful part of grammar. Commas, periods, and question marks organize sentences and signal pauses. Proper punctuation in emails or reports can prevent misinterpretation and make your writing more professional.
Avoid Overuse of Passive Voice
While passive voice is grammatically correct, overusing it can make sentences less direct. Active voice usually sounds more natural in daily writing. For example, “The manager approved the report” is clearer than “The report was approved by the manager.”
Practical Grammar Tips for Speaking
Grammar in speaking is less formal but equally important. Clear speech requires correct sentence patterns, verb forms, and word order.
Speak in Complete Sentences
Even in casual conversation, try to speak in complete sentences when possible. This habit helps listeners understand you better and reduces the chance of miscommunication. For example, instead of saying “Yesterday… went park,” say “Yesterday I went to the park.”
Use Contractions Naturally
Contractions like “I’m,” “don’t,” and “we’re” make spoken English sound natural. They also help you speak faster and more fluently without breaking grammar rules.
Listen and Repeat
Listening to native speakers and repeating phrases can improve both pronunciation and grammar instincts. Focus on how sentences are structured and try to mimic the rhythm and word order. This builds practical grammar skills that feel intuitive rather than forced.
Practice Common Phrases
Everyday conversations often rely on recurring phrases and sentence patterns. Learning these phrases helps you apply grammar correctly without thinking too much. For example, “I have been to…,” “Can you help me with…,” and “I would like to…” are widely used in daily speech.
Integrating Grammar Into Daily Life
The key to mastering practical grammar is integration into daily activities. Grammar is learned best when used actively rather than studied passively.
Writing Journals or Notes
Keeping a journal or writing daily notes in English encourages the practical application of grammar rules. Even simple entries like “Today I went to the market and bought fruits” reinforce sentence structure and tense usage.
Speaking With Friends or Online Partners
Conversing with others in English provides real-time feedback and forces you to use correct grammar spontaneously. Online language exchange platforms or conversation clubs can provide low-pressure environments to practice.
Reading Regularly
Reading books, articles, and even social media posts exposes you to correct grammar in context. Notice sentence structures, punctuation, and tense usage as you read. Over time, these patterns become intuitive.
Revising Your Writing
Always take time to review your writing. Checking for tense consistency, subject-verb agreement, and sentence clarity turns mistakes into learning opportunities.
The Role of Grammar in Confidence and Professional Growth
Practical grammar is not just about correctness; it is about confidence and credibility. Clear writing and speech create a professional image, whether in emails, presentations, or interviews. People are more likely to understand and trust you when your communication is grammatically sound.
For learners, every small improvement in grammar strengthens confidence. When you know you are understood, you can focus on expressing ideas, telling stories, or persuading others rather than worrying about mistakes.
Conclusion
Practical English grammar is essential for effective daily writing and speaking. By focusing on common challenges like tenses, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure, learners can communicate clearly and confidently. Applying grammar in everyday writing, speaking, and reading activities reinforces learning and makes it feel natural.
Remember, grammar is a tool, not a burden. Simple and consistent practice can make a huge difference, allowing you to express ideas fluently, make a strong impression, and build confidence in both personal and professional settings.
By understanding and using practical grammar rules, anyone can transform everyday communication into a clear, confident, and professional skill. The key is regular use, active practice, and paying attention to how language works in real-life situations.
Understanding English Grammar Through Real Usage Examples
Understanding English Grammar Through Real Usage Examples – Learning English grammar can often feel overwhelming. Rules, exceptions, and endless verb forms can make even the most enthusiastic learners feel stuck. But the secret to mastering English grammar isn’t memorizing every rule—it’s seeing how English is actually used in real life. When you study grammar through real usage examples, you not only understand the rules but also learn how to apply them naturally in conversation and writing.
Why Real Examples Matter More Than Rules
Traditional grammar books tend to focus on rules and charts. While this is useful, it can also be limiting. Grammar doesn’t exist in a vacuum; it comes alive when it’s part of a sentence, a story, or a conversation. Real usage examples help learners see patterns in how native speakers actually communicate.
For instance, consider the present perfect tense. A rule book might tell you it is formed with “has/have + past participle.” But seeing sentences like, “I’ve visited Paris three times” or “She hasn’t called me today” makes the concept clear in context. You understand not just the structure, but also the situations in which it is naturally used.
Using Context to Remember Grammar
One of the most effective ways to internalize grammar is through context. Context helps your brain connect the rule to its practical use, making it easier to recall when speaking or writing.
Take prepositions, for example. They are notoriously tricky because they rarely translate directly between languages. By studying sentences like, “He is interested in music” or “She is good at drawing,” you start to see patterns rather than memorizing lists of prepositions. These small, repeated examples from real conversations can dramatically improve your fluency.
The Power of Listening and Reading
Another way to encounter real examples is through listening and reading. Movies, podcasts, and everyday conversations are treasure troves of natural English. Even reading books, news articles, and blogs exposes you to grammar in action. You notice how adjectives are used, how tenses shift in storytelling, and how questions and negations are formed.
The key is to pay attention to the patterns. Don’t just read; observe. Highlight sentences that feel natural or particularly expressive. Later, try to use them in your own writing or speaking. Over time, these patterns become second nature.
Common Grammar Points Made Clear Through Examples
Certain grammar points can be tricky, but examples make them much easier to grasp. Here are a few cases:
Articles: a, an, and the
Articles are small words but cause big headaches for learners. Seeing them in context is crucial. For example, “I saw a cat in the garden” versus “The cat in the garden was sleeping” shows how the article changes meaning. Real examples demonstrate when to use “a” for general mentions and “the” for specific ones.
Conditionals in Everyday Speech
Conditionals can also be confusing. By observing sentences like, “If it rains, we will stay inside” or “If I were rich, I would travel the world,” learners see the structure and meaning clearly. Real conversations often mix zero, first, second, and third conditionals naturally, which helps learners understand the subtle differences.
Common Verb Tenses
Verb tenses are more than just rules; they are tools for expressing time and intention. Examples like, “I am reading a book” versus “I read that book last week” demonstrate the difference between present continuous and simple past instantly. The more examples you encounter, the more intuitively you grasp tense usage.
Making Examples Work for You
Seeing examples is just the first step. The next step is actively using them. Try to mimic sentences you encounter, replacing words to suit your own ideas. This practice strengthens memory and fluency.
For example, if you learn the sentence, “She has been working here for five years,” try changing it: “He has been studying English for two months” or “They have been living in London since 2020.” This method reinforces grammar patterns and makes them feel natural rather than forced.
Writing and Speaking Exercises
One of the most effective ways to internalize grammar through examples is by writing short paragraphs or dialogues using sentences you have learned. Even speaking to yourself using these sentences helps solidify patterns in your mind.
Reading aloud is also a great tool. It helps you notice rhythm, intonation, and natural pauses that are often lost in silent reading. Over time, speaking and writing become easier because your brain has a ready-made library of real examples to draw from.
Why This Approach is Better for Long-Term Learning
Studying grammar through real examples is more sustainable than memorizing rules alone. When learners rely only on rules, they often forget them in real-life situations. Real examples create mental associations, turning grammar from abstract rules into usable language.
Moreover, using examples helps you sound more natural. You start to develop an ear for how native speakers talk, which reduces the common mistake of overthinking grammar while speaking. This approach also encourages learners to experiment with language in a safe way, building confidence and fluency.
Conclusion
Understanding English grammar doesn’t have to be a chore. By focusing on real usage examples, you learn grammar in context, making it easier to remember and use naturally. Listening, reading, writing, and speaking with examples in mind will gradually transform your skills from mechanical repetition to fluid, confident communication.
So next time you study a grammar point, don’t just memorize the rule. Look for examples, notice patterns, and practice creating your own sentences. Grammar becomes not a set of obstacles but a toolkit for expressing yourself clearly and confidently in English.
By embracing this approach, English learners can finally move past theory and into real, practical language use, making their learning experience enjoyable, effective, and long-lasting.